Price floor and price ceiling draft.
Price floor and price ceiling questions.
A price ceiling example rent control.
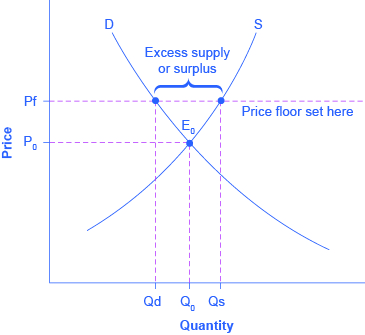
Terms in this set 7 price floor a price floor is a government set price above equilibrium price it is a tax on consumers and a subsidy to producers.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
What does this graph show.
10 questions show answers.
This is usually done to protect buyers and suppliers or manage scarce resources during difficult economic times.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
This quiz worksheet combination will test your understanding of price ceilings and price floors.
This is the currently selected item.
Price ceilings and price floors.
The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
The opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor which sets a minimum price at which a product or service can be sold.
Quiz questions will focus on topics such as binding price ceiling lines and the term given to how.
Price floors and ceilings are inherently inefficient and lead to sub optimal consumer and producer surpluses but.
Final exam ch.
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
Price floors and price ceilings are government imposed minimums and maximums on the price of certain goods or services.
Real life example of a price ceiling.
If a price floor was set at 320 what quantity would be purchased.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
Taxation and dead weight loss.